A bank is a business that accepts deposits of money, and sells financial services such as loans, mortgages, checking services, credit card services and individual retirement accounts. If you work in the US and don't like the idea of hiding cash under a mattress, you must deal with a bank sooner or later.
Banks offer a variety of accounts to meet different customers' needs. The following are the most common:
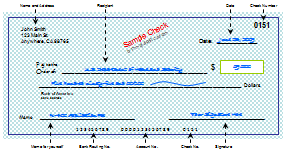
Simply speaking, a check is a piece of paper, preprinted with your name and address, bank routing number, checking account number and a check number. When writing a check, you need to fill out four blank areas: to whom the money is going to ("to the order of"), the date, the amount of money that is being transferred, and your signature to authorize the transaction. You may also write a brief memo on the check.
Since a thief can forge your signature and transfer your money to their account, you want to safe guard your personal checks. If you happen to lose them, contact your bank immediately and cancel the checks, or close the checking account altogether. In this case your checks become worthless, making them much safer than cash.
Electronic banking simply means that you can do certain banking services electronically, without the need of having to go to a physical bank. It has made everyone's life so much easier that today, every bank offers some types of electronic banking.
Over the past few years a new type of banks have emerged: they do not have any "brick and mortar" branches your can walk into. They are "virtual" banks.
Since an internet bank only does business online, its operating cost is lower than traditional banks, and may be able to pass on the savings to their customers. This means you could be getting a better rate, lower fees, free perks and the like.
One concern many people have with online/internet banking is that personal data are constantly transmitted among various networks. To limit your risk, you want to review a bank's privacy statement carefully, "opt out" to limit sharing of your information, and check to see if they have high level security measures in place.
Debit cards look just like credit cards, but they are completely different. If you pay with a debit card, the amount of purchase is electronically deducted from your bank account. There will be no monthly bill like that of credit cards, because you have already paid for the purchases almost immediately. Debit cards may also function as ATM cards.
A bank is a business, and businesses may fail. So what happens to your money if your bank goes bankrupt? The answer is FDIC, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, that offers insurance coverage for your deposits. If your "member FDIC" bank fails, all your deposits at that bank will be reimbursed by the FDIC for up to $250,000.
Although most deposit accounts are insured by the FDIC, including savings, checking, CD, IRA, MMA, etc., your investment accounts at the same bank are not! Your investment in mutual funds, stocks, annuities and other non-deposit products are not covered by the FDIC.
Yes. There are typically commercial banks, savings banks and credit unions. Although they used to concentrate on serving different customers, today they offer many of the same services to the general public. It is unlikely that you will notice any difference when you do business with them.
For example, a credit union is actually classified as a thrift institution, rather than a bank. Credit unions still require membership, but many also offer business loans and home mortgages, just like commercial banks.
Ask the following questions and do comparison shopping before choosing a bank: